Updates on AI Hypercomputer from Google Cloud Next 25
Advancements in AI with Google Cloud’s Hypercomputer
Google Cloud has made significant strides in enhancing its AI capabilities through the introduction of the AI Hypercomputer. This innovative technology is specifically designed to support complex AI workloads, making it an attractive option for cloud customers engaged in demanding computational tasks. By optimizing both hardware and software, Google Cloud aims to provide improved efficiency in training and inferencing processes.
Latest Upgrades Announced at Google Cloud Next 25
During the recent Google Cloud Next 25 event, several updates were unveiled that enhance the architecture of the AI Hypercomputer. These advancements are geared towards maximizing performance and minimizing costs associated with AI operations.
AI-Optimized Hardware
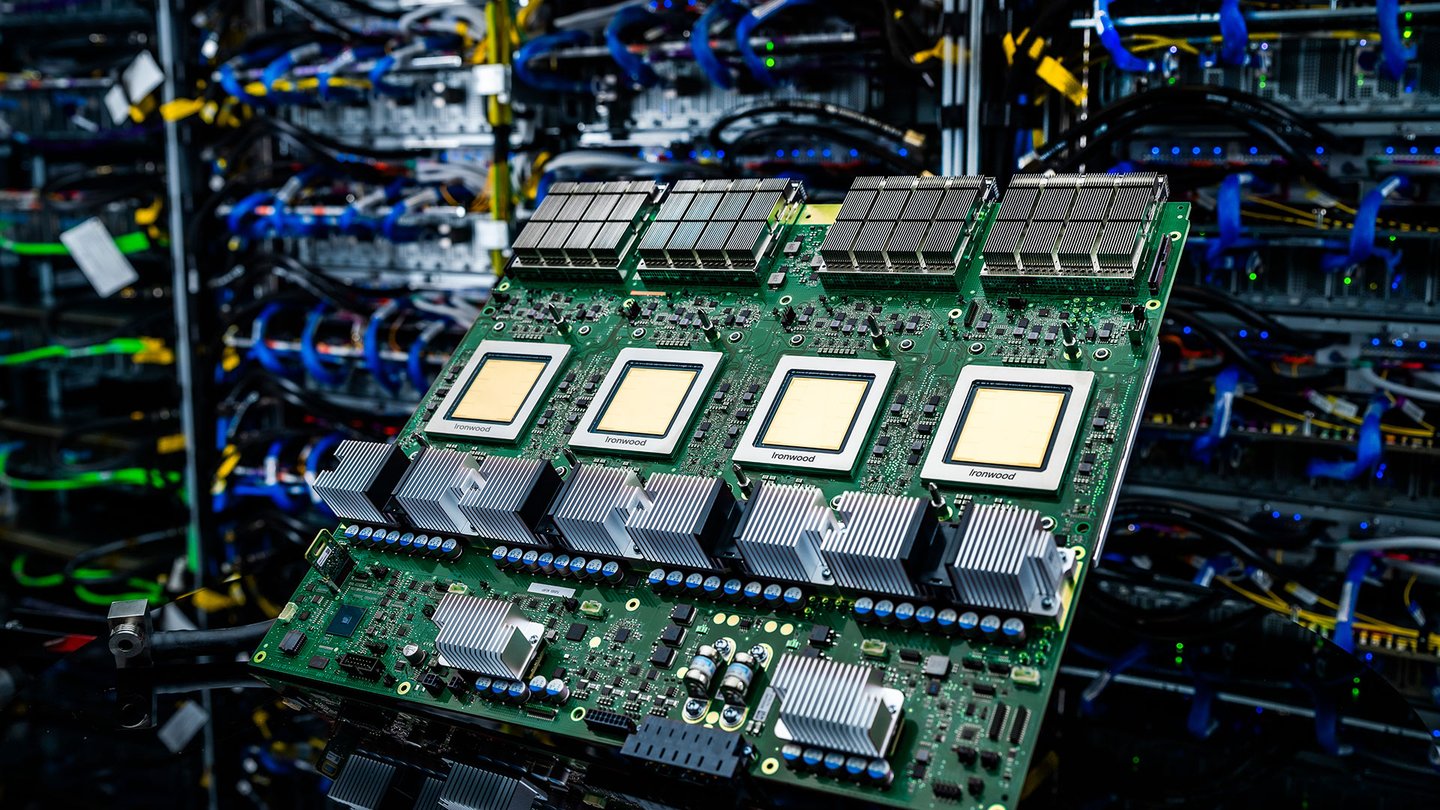
One of the key highlights of the updates is the launch of the seventh-generation Tensor Processing Unit (TPU) known as Ironwood. This advanced hardware is meticulously engineered for both thinking and inferential AI applications.
- Enhanced Compute Capacity: Ironwood provides a remarkable five times increase in peak compute capacity compared to its predecessor. This upgrade means that users can handle larger models and datasets more efficiently.
- Improved Memory Capacity: In addition to its compute capabilities, Ironwood boasts six times the high-bandwidth memory (HBM) capacity of the previous generation. This enhancement allows for faster data retrieval and processing, which is essential for AI workloads that require significant memory for operations.
Software Improvements for Inference
Google’s commitment to enhancing its AI Hypercomputer is also reflected in the software layer updates designed for inference tasks. These improvements are focused on optimizing compute resource usage, leading to accelerated AI workflows.
- Faster Development Cycles: By streamlining software processes, developers can expect a reduced time span between the training and inference stages. This means quicker iteration cycles for AI models, enabling faster deployment and real-world application.
- Resource Optimization: The software improvements allow businesses to make more efficient use of their existing resources, reducing operational costs and maximizing performance.
Flexible Consumption Options
To further assist businesses in managing their AI expenditures, Google has introduced flexible consumption models within its Dynamic Workload Scheduler. This feature provides several options for organizations to choose from, allowing for tailored solutions based on their specific needs.
- Cost Management: With these flexible models, companies can better control their costs associated with AI infrastructure. This adaptability helps organizations align their spending with actual usage, which is particularly beneficial for those with variable workloads.
- Scalability: The consumption options also support scalability, enabling businesses to adjust their resources as demand fluctuates without incurring unnecessary costs.
Additional Information
For those interested in learning more about these updates and how they can impact AI operations, detailed insights can be found on the Google Cloud blog. This resource provides in-depth explanations and further information related to the capabilities and advantages of the AI Hypercomputer, ensuring that stakeholders stay informed about cutting-edge developments in cloud AI technology.
In summary, Google Cloud’s advancements in its AI Hypercomputer signify a strong commitment to supporting the needs of cloud customers engaged in complex and demanding AI workloads. The introduction of the Ironwood TPU, software updates, and flexible consumption options collectively enhance the overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness of AI operations in the cloud.





