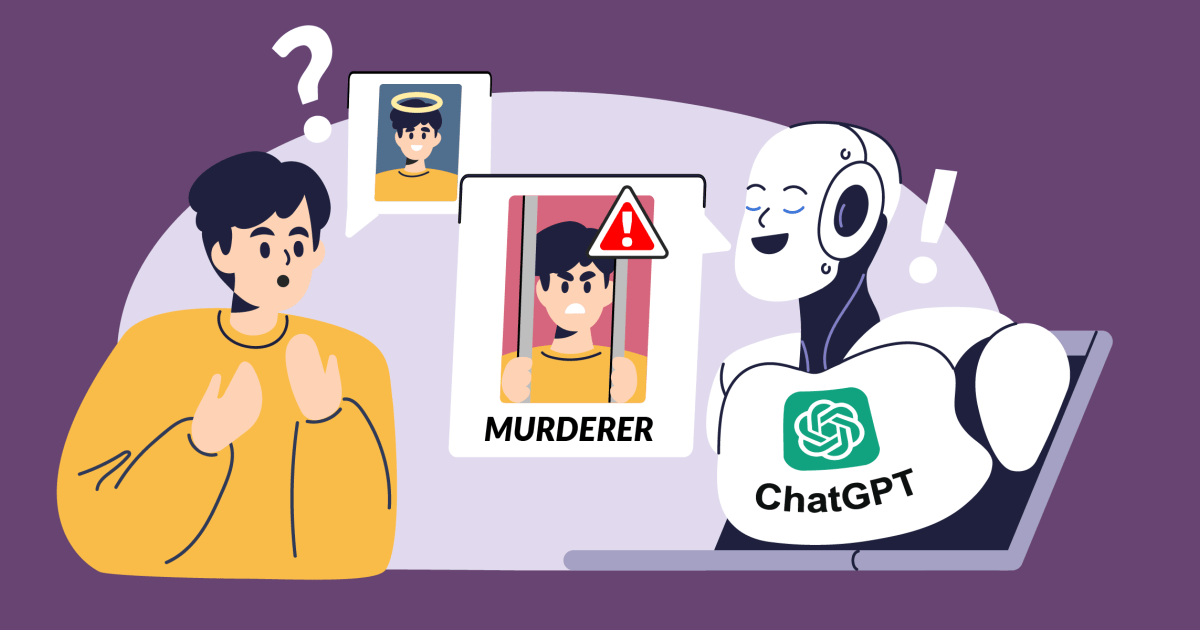
ChatGPT Fabricates a Fictional Child Murderer
Concerns Over ChatGPT and Data Accuracy
Introduction
The accuracy of information generated by AI systems like ChatGPT has come under scrutiny. Arve Hjalmar Holmen, a complainant, expressed significant concern over how some individuals might believe incorrect information presented by the model. "Some think that ‘there is no smoke without fire’. The fact that someone could read this output and believe it is true, is what scares me the most," Holmen stated, highlighting the dangers of misinformation.
The Hallucination Problem
Misleading Information
In April 2024, the European non-profit organization, noyb, lodged a complaint regarding the inaccuracies propagated by AI models, focusing specifically on what they termed “hallucinations.” These are instances where the AI generates false or misleading information. Holmen’s case involved an incorrect date of birth for a public figure. When noyb approached OpenAI to correct this misinformation, the response was that they could only "block" specific prompts but would not fully erase the erroneous data from the system.
GDPR Compliance Issues
While the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) mandates data accuracy, OpenAI’s attempt to circumvent these obligations by including a disclaimer about potential mistakes does not negate their legal responsibilities. Kleanthi Sardeli, a data protection lawyer at noyb, pointed out that such disclaimers do not absolve AI companies from the law. "If hallucinations are not stopped, people can easily suffer reputational damage," she added, emphasizing the urgency to address this issue.
Updates to ChatGPT
Official Search Engine
In response to the concerns raised, OpenAI has made updates to ChatGPT. The model can now search the internet for accurate information about individuals when queried. This means that, for Holmen, ChatGPT no longer falsely brands him a murderer; however, the risk of incorrect data still lingers within the model’s training dataset.
Data Processing Concerns
It is important to note that ChatGPT utilizes user data for improving its model. There is currently no system in place to guarantee that misinformation can be completely removed without retraining the entire model. Furthermore, OpenAI does not comply with the right to access user data as detailed under Article 15 of GDPR, leaving users unable to confirm what data is processed internally. This situation contributes to the anxiety experienced by individuals subject to erroneous outputs.
Legal Action in Norway
Filing a Complaint
Given the ongoing challenges, noyb has filed a complaint with the Norwegian Data Protection Authority (Datatilsynet). The organization argues that allowing AI models to produce defamatory outputs violates the accuracy principle outlined in Article 5(1)(d) of GDPR.
Requested Actions
noyb is urging Datatilsynet to mandate OpenAI to delete the defamatory information and make necessary adjustments to their model to prevent future inaccuracies. The organization also seeks administrative fines to deter similar violations.
Impact on Users
Personal Consequences
The implications of incorrect AI outputs can be severe for individuals. Mischaracterization by automated systems can lead to lasting reputational damage, and the inability to correct such inaccuracies raises significant concerns about user rights and data protection. The case of Holmen exemplifies the broader issue of accountability for AI-generated information.
Need for Changes in AI Practices
As the landscape of AI continues to evolve, it’s crucial that companies like OpenAI adopt more rigorous practices to ensure data accuracy. Addressing these challenges is not just a legal obligation; it’s essential for maintaining user trust and protecting individuals from potential harm.






