Review of Concerns Surrounding the Implementation of AI Applications in Dentistry
Study Selection and Search Results
The research process involved an extensive electronic search across major databases like PubMed and Scopus. Initially, a total of 776 studies were discovered. After eliminating 51 duplicate records, 725 studies remained. A significant number—665 studies—were excluded due to irrelevant titles. Ultimately, 60 studies were assessed through abstract and full-text screenings, leading to the selection of 34 studies from the electronic search. In addition to this approach, a manual search via Google Scholar uncovered 123 studies, out of which 10 were also included. This brought the total count of studies for this review to 44.
Summary Characteristics of Studies
The studies included in this review were published between 2011 and 2024. Most had sample sizes ranging from 10 to 68 patients. Among the 44 analyzed studies:
- Retrospective Studies: 26 of the studies were retrospective in nature.
- Comparative Studies: 7 studies employed a comparative design.
- Observational Studies: 3 studies observed various phenomena.
- Validation Studies: 5 studies sought to validate methodologies.
- Cross-Sectional Studies: 2 studies represented cross-sectional designs.
- Prospective Study: 1 prospective study was also part of the analysis.
Notably, the AI-based applications examined utilized various tools, with Diagnocat being the most prevalent, featured in 26 studies. CephX followed closely, appearing in 16 studies.
Distribution by Specialty
The studies were categorized based on their focused specialties:
- Orthodontics: 20 studies.
- Endodontics: 7 studies.
- Dental Radiology: 6 studies.
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery: 5 studies.
- Prosthodontics: 2 studies.
- Periodontics: 2 studies.
- Restorative Dentistry: 1 study.
- Oral Medicine: 1 study.
Contacting Companies
To gain further insight into AI-driven applications for dental practices, various AI companies claimed to offer their services to dental professionals. The companies contacted included:
- Smilo.AI
- Smile.AI
- Videa.AI
- Diagnocat
- Denti.AI
- Smile Designer
- Overjet
- CephX
- Pearl
- DentalXR.ai
Despite reaching out multiple times via email, only the CephX company responded, offering a free trial instead of comprehensive access. This limitation restricted the ability to assess real-world deployment fully.
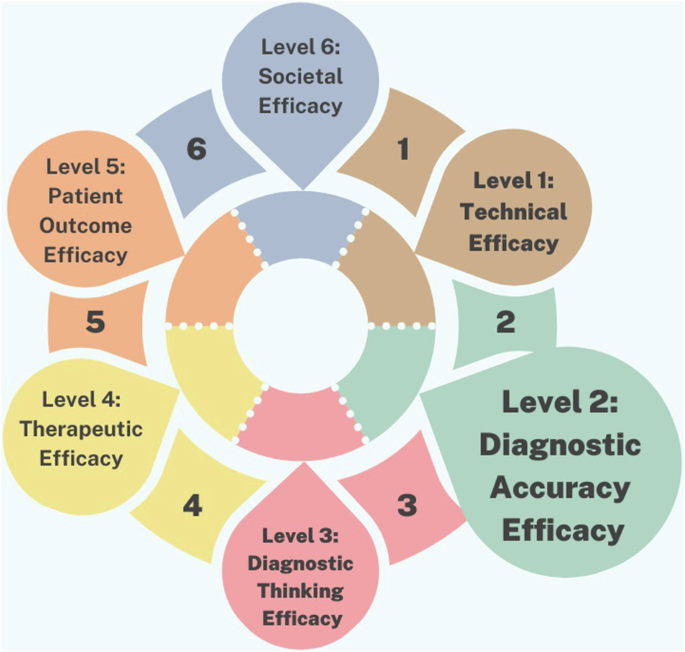
Deployment Levels in Studies
The studies were categorized according to different deployment levels, which reflect varying stages of assessment and application:
- Level 1 (Technical Reports): These studies focus on the technical efficacy of AI, primarily evaluating algorithm performance and accuracy in lab settings.
- Level 2 (Diagnostic Accuracy): These studies emphasize how well AI can diagnose conditions compared to human experts, assessing metrics like sensitivity and specificity.
Higher deployment levels are comparatively sparse:
- Level 3 (Diagnostic Thinking): Evaluates how AI contributes to clinical decision-making.
- Level 4 (Therapeutic Efficacy): Assesses the effectiveness of AI in treatment protocols.
- Levels 5-6 (Patient Outcome and Societal Efficacy): Focus on the broader impact of AI applications in real-world settings and their overall benefit to society.
Ultimately, 27 of the studies primarily focused on Level 1 and Level 2, indicating that further exploration into higher levels of deployment is necessary for a more comprehensive understanding of AI’s potential in dental applications.