Alibaba Introduces Qwen 3, a Series of ‘Hybrid’ AI Reasoning Models
Alibaba Introduces Qwen 3: A New Family of AI Models
On Monday, Alibaba, the renowned Chinese technology corporation, unveiled its latest innovation: Qwen 3, a series of artificial intelligence models. The company asserts that these models not only compete with but in several instances outperform leading models from Western tech giants like Google and OpenAI.
Availability and Features of Qwen 3 Models
Most versions of the Qwen 3 models will soon be accessible for download under an open license on platforms such as Hugging Face and GitHub. The models vary in size, from 0.6 billion parameters to a staggering 235 billion parameters. Typically, a model’s performance improves with an increase in parameters: more parameters often equate to better problem-solving capabilities.
Impact on Global AI Competition
The rise of Qwen 3 signifies an intensifying competition in the artificial intelligence landscape, putting additional pressure on American research labs like OpenAI to enhance their offerings. This competitive shift has prompted policymakers to enact more stringent measures in an attempt to control the export of essential chips to Chinese AI firms, which are critical for training such advanced models.
Hybrid Model Capabilities
Alibaba describes its Qwen 3 models as "hybrid" because they can alternate between fast responses for simpler queries and more thoughtful problem-solving for complex issues. This reasoning ability helps the models verify their own information, akin to OpenAI’s models, though this might result in a slightly slower response time.
The Qwen team elaborated in a recent blog post, stating, "We have seamlessly integrated thinking and non-thinking modes, offering users the flexibility to control the thinking budget." This adaptability caters to different user needs, allowing for a balance between speed and depth of comprehension.
Training Data and Performance Enhancements
The Qwen 3 models were trained using an extensive dataset comprising nearly 36 trillion tokens. Tokens represent fragments of data that the models analyze; for perspective, one million tokens translate to about 750,000 words. Alibaba notes that this extensive training included various materials such as textbooks, question-answer pairs, and programming code, which collectively enhance the models’ ability to understand and process information.
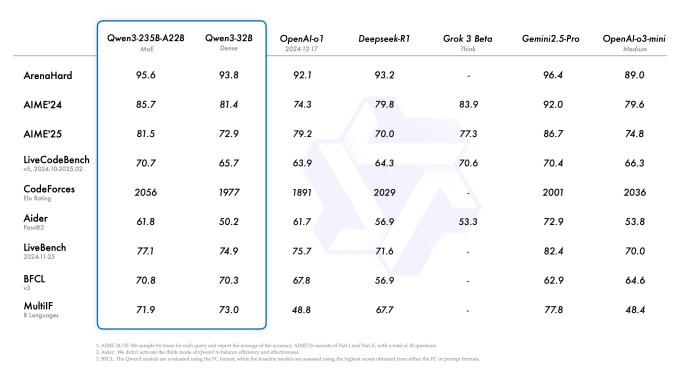
These advancements have significantly improved Qwen 3’s performance compared to its predecessor, Qwen 2. For instance, in competitive programming settings like Codeforces, the largest Qwen 3 model, known as Qwen-3-235B-A22B, demonstrated superior performance against OpenAI’s o3-mini. Additionally, it excelled in various math challenges and reasoning tests, indicating its robust capabilities.
Current Availability
As of now, while the Qwen-3-235B-A22B model shows outstanding performance, it is not yet publicly accessible. Conversely, the Qwen3-32B model, which is publicly available, remains competitive against other proprietary AI models, including those from DeepSeek and OpenAI. It even surpasses OpenAI’s o1 model in several evaluation metrics, including an accuracy assessment called LiveBench.
Capabilities and Cloud Availability
According to Alibaba, Qwen 3 stands out in tasks involving tool interaction, following specific instructions, and format copying. Beyond direct downloads, these models are also being offered through cloud services, including platforms like Fireworks AI and Hyperbolic, allowing for broader accessibility and application.
Industry Perspectives
Tuhin Srivastava, co-founder and CEO of AI cloud host Baseten, remarked that Qwen 3’s release is a pivotal development in the trend of open models keeping pace with their closed-source counterparts. He noted that despite the U.S. government imposing limits on chip sales to China, models like Qwen 3, which are cutting-edge and accessible, will likely find domestic applications within various sectors.
This development highlights a critical moment in the evolving landscape of AI technology, where open-source models are beginning to match the capabilities of those found in more closed systems.




