Google DeepMind Improves AMIE for Ongoing Disease Management
Google DeepMind Expands AMIE for Longitudinal Disease Management
Google DeepMind has made significant strides in enhancing its Articulate Medical Intelligence Explorer (AMIE) by broadening its functionality beyond just diagnostics. The upgraded system now plays a vital role in supporting healthcare professionals with ongoing disease management. AMIE is tailored to aid clinicians in tracking disease development, modifying treatment plans, and ensuring compliance with clinical guidelines throughout multiple patient visits.
New Two-Agent Framework of AMIE
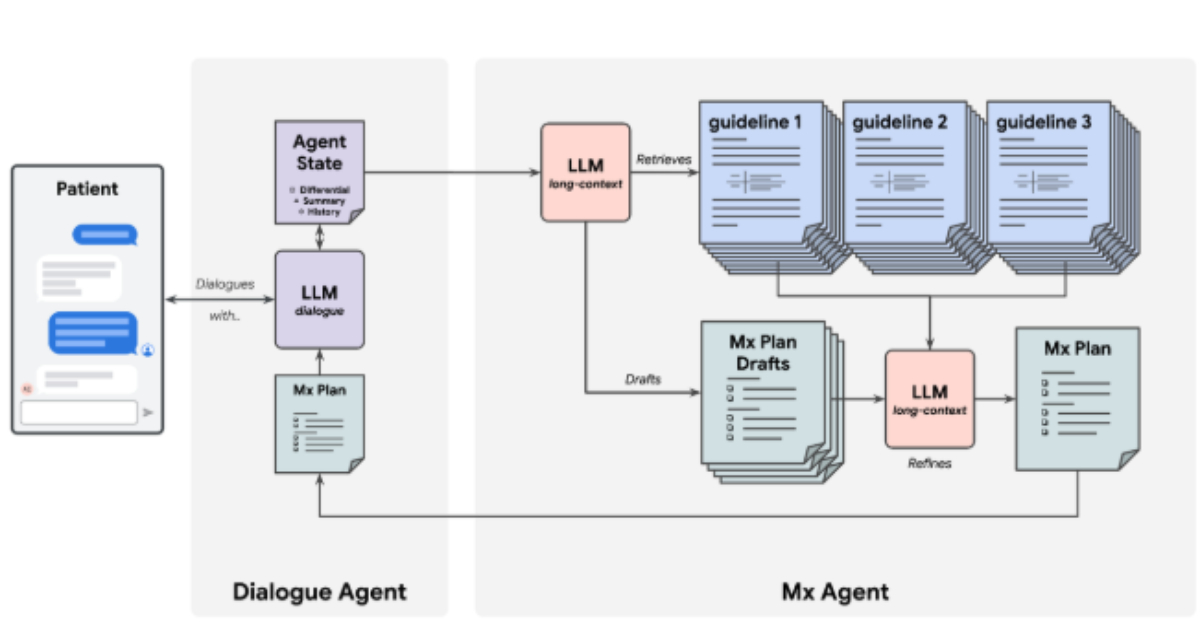
The latest framework for AMIE introduces a two-agent model designed to improve how healthcare professionals interact with the system:
Dialogue Agent: This component oversees communication with patients, gathers clinical information, and ensures that conversations are consistent at every visit.
- Management Reasoning (Mx) Agent: This agent analyzes clinical data, applies relevant guidelines, and reviews patient histories to formulate structured treatment and monitoring plans.
This innovative approach is built on DeepMind’s Gemini AI model, which utilizes long-context processing to examine multiple patient interactions, integrate new clinical data, and align advice with established clinical guidelines, including those from the UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) and BMJ Best Practice.
Potential for Broader Healthcare Applications
Giancarlo Nicola Zaccaria, a technical program director at Wellhub, expressed enthusiasm for AMIE’s two-agent structure, noting that it opens doors to tackle various healthcare challenges. His acknowledgment underscores the transformative potential of this technology in enhancing patient care and operational efficiency.
Effectiveness of AMIE: Recent Studies
To assess AMIE’s capabilities, researchers conducted a randomized, blinded virtual objective structured clinical examination (OSCE). This study involved 20 primary care physicians (PCPs) across 100 multi-visit case scenarios. During the evaluation, specialist physicians, who were unaware of the source of the management plans, rated AMIE’s recommendations as comparable to those of human PCPs. Notably, AMIE showcased significant advancements in treatment accuracy, effectively selecting appropriate diagnostic tests while minimizing unnecessary ones, leading to improved patient management practices.
RxQA: New Benchmarking Dataset
DeepMind further introduced RxQA, a comprehensive benchmarking dataset that consists of 600 multiple-choice questions sourced from national drug formularies. AMIE exhibited robust performance in critical medication-related areas, including indications, contraindications, dosing, and safety assessments. This performance further demonstrates AMIE’s relevance in the healthcare landscape.
Shan Rizvi, who focuses on AI-enhanced healthcare solutions, noted the potential integration of AMIE into his private patient care model. He aims to reduce physician burnout and enhance doctor-patient collaboration for improved health optimization through the use of AI Assistants, Agents, and Operators.
Future Research Directions
Though the initial evaluation of AMIE has been conducted in a controlled setting, there are limitations. Real-world challenges such as integration with electronic health records, variations in patient behavior, and discrepancies across healthcare systems remain unaccounted for. Upcoming research will aim to explore the practical effectiveness of AMIE within clinical environments, assessing its potential to influence physician decision-making positively.
The recent enhancements to AMIE mark a significant development in utilizing AI for clinical reasoning, emphasizing a systematic management approach over time. Continued validation in practical healthcare settings will be critical in determining its efficacy and reliability for medical practices.