Meta Introduces LlamaFirewall Framework to Prevent AI Jailbreaks, Injections, and Security Vulnerabilities
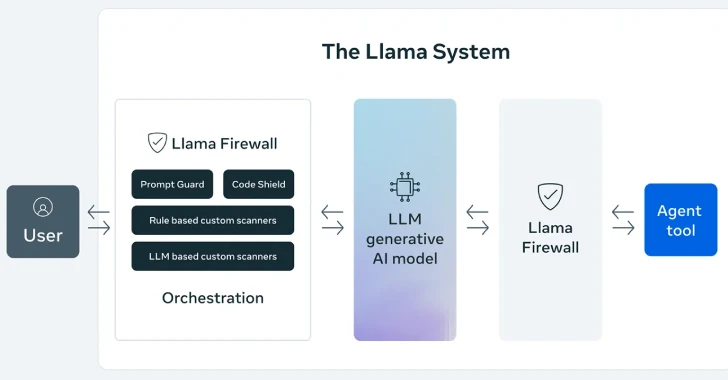
Introduction to LlamaFirewall
On April 30, 2025, Meta announced a significant new framework called LlamaFirewall, aimed at enhancing the security of artificial intelligence (AI) systems. This open-source framework is designed to combat emerging cyber threats, including prompt injection attacks, jailbreaks, and the creation of insecure code.
Key Features of LlamaFirewall
LlamaFirewall integrates three primary security measures:
- PromptGuard 2
- Agent Alignment Checks
- CodeShield
Let’s delve into each component to understand how they contribute to securing AI applications.
1. PromptGuard 2
PromptGuard 2 is particularly focused on real-time vigilance against prompt injection and jailbreak techniques. These tactics can exploit vulnerabilities in AI systems, allowing malicious actors to manipulate the AI’s responses or behavior. By detecting such threats as they arise, PromptGuard 2 provides an essential layer of security that protects both the AI and its users.
2. Agent Alignment Checks
The Agent Alignment Checks feature inspects the reasoning processes of AI agents. It identifies potential risks like goal hijacking, which can occur when an agent is led to pursue unintended objectives. This feature also addresses indirect prompt injection scenarios, ensuring that the AI remains aligned with its intended purpose and does not veer off course due to manipulative inputs.
3. CodeShield
CodeShield acts as a static analysis tool aimed at preventing the generation of insecure or harmful code by AI systems. It meticulously reviews the code that AI generates, flagging potential security issues before they can contribute to vulnerabilities or exploits.
Modular Architecture
Meta has crafted LlamaFirewall with a modular architecture, allowing security teams and developers to create tailored defenses. This setup enables a comprehensive approach, spanning from the initial processing of user input to the final outcomes generated by AI systems. This flexibility is especially crucial for both straightforward chat models and complex autonomous agents.
Leveraging Existing Tools
Alongside LlamaFirewall, Meta has released updated versions of several important tools:
- LlamaGuard
- CyberSecEval
These updates are intended to enhance the detection of harmful content and measure the cybersecurity capabilities of AI systems.
CyberSecEval 4
The latest version of CyberSecEval introduces a new benchmark called AutoPatchBench. This innovation assesses the ability of large language models (LLMs) to automatically address various vulnerabilities in C/C++ code identified through fuzzing techniques. The goal of AutoPatchBench is to standardize the evaluation of AI tools that assist in vulnerability repairs.
New Initiative: Llama for Defenders
Additionally, Meta has introduced a program named Llama for Defenders. This initiative supports AI developers and partner organizations by offering access to both open-source and proprietary AI solutions. Its focus is on tackling specific security challenges, such as detecting AI-generated scams, fraud, and phishing attempts.
Privacy Considerations
In a related development, WhatsApp has previewed a technology called Private Processing. This feature aims to utilize AI capabilities without sacrificing user privacy. By processing requests in a secure environment, it ensures that sensitive user data remains protected.
Both LlamaFirewall and these other initiatives underscore Meta’s commitment to advancing security in AI technologies. They are actively engaging with the cybersecurity community to refine their approaches and strengthen the overall security of AI systems. This collaborative effort aims to create safer environments for users interacting with AI applications.






