New Study Reveals AI Search Engines Inaccurately Cite Sources in More Than 60% of Tests
AI Search Engines and Citation Challenges: A Recent Study
Overview of the Issue
In recent months, AI chatbots, particularly those powered by search engines, have faced serious criticism for their ability to correctly cite sources. This concern primarily stems from reports indicating that these systems often fail to accurately reference news publishers. A study conducted by the Tow Center for Digital Journalism at Columbia University has brought new insights into this pressing issue.
Study Details
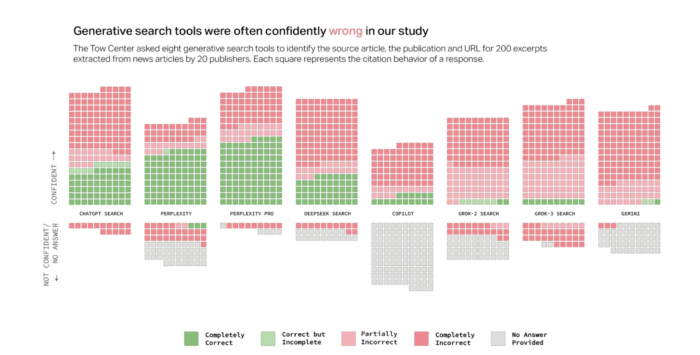
On March 6, 2025, researchers Klaudia Jaźwińska and Aisvarya Chandrasekar released their findings in a study titled "AI Search Has a Citation Problem." The researchers assessed eight different AI search engines, including ChatGPT Search, Perplexity, Gemini, and Copilot, among others. They devised a set of 200 tests where each search engine was tasked with retrieving information based on given quotes from articles. The results were alarming: the engines failed to provide the correct information over 60% of the time across 1,600 queries.
Performance of AI Search Engines
Success Rates
- Perplexity: This engine recorded the lowest failure rate, providing incorrect responses only 37% of the time.
- Grok-3 Search: The performance here was significantly poorer, with a staggering failure rate of 94%. Strikingly, Grok-3 was one of the more expensive services, costing around $40 per month, yet it performed worse than its predecessor Grok-2, which is available for free.
Overconfidence in Responses
Another significant finding from the study was the overconfidence exhibited by many AI chatbots in their responses. While some AI systems are programmed to indicate uncertainty when they lack information, many popular engines often provide answers with unwarranted confidence. For instance, of the 134 incorrect citations analyzed for ChatGPT, the chatbot used disclaiming language only in 15 instances. In contrast, Copilot mostly refrained from answering questions altogether.
Problems with URLs
The study also revealed persistent problems with the URLs provided by these AI systems. Broken or incorrect links were a common issue, particularly for Gemini and Grok-3, which often redirected users to "404 error" pages. In fact, Grok-3 cited non-existent pages 154 times during the tests.
Traffic Generation Concerns
The troubling citation problems inch closer to larger questions about the effectiveness of AI search engines in driving traffic to news publishers. Findings from a recent study by TollBit highlighted that chatbots, on average, generate referral traffic that is 96% less effective than traditional Google search results. Additionally, an analysis of ChatGPT and Perplexity from Northwestern University showed that only 3.2% of filtered traffic for news publishers came from ChatGPT, with Perplexity providing a slightly better figure at 7.4%.
Implications for News Publishers
The research findings raise critical concerns regarding the viability of AI search engines as reliable sources of referral traffic for news outlets. Unless AI companies can resolve the citation accuracy issues currently plaguing their engines, it seems unlikely that these platforms will replace traditional search methods effectively.
For those interested in a deeper dive into the study, you can access the full report titled "AI Search Has a Citation Problem" through the Columbia Journalism Review.






