The Impact of A.I. on Computer Development Worldwide
The Transformation of Computing Driven by Artificial Intelligence
The landscape of computing is undergoing one of the most significant transformations since the establishment of the World Wide Web. Just as companies adapted their systems to accommodate the internet boom in the 1990s, they are now revamping their infrastructures to harness the power of artificial intelligence (AI). This change spans from the smallest electronic components to large-scale data center designs, fundamentally reshaping how computing is approached.
The Rise of Data Centers
Over the last two decades, major technology companies have erected numerous data centers worldwide. These facilities house numerous computers designed to manage the increasing online traffic for services such as search engines, email, and e-commerce. However, the current wave of data centers is set to be dramatically more advanced.
For example, Google’s first data center, established back in 2006 in The Dalles, Oregon, cost approximately $600 million. In stark contrast, OpenAI, along with its partners, has announced a plan to invest about $100 billion in new facilities, starting with a large campus in Texas, aiming to eventually pour in an additional $400 billion across the United States.
Economic and Community Impacts
This seismic shift in computing impacts not only technology but also finance, energy resources, and local communities. Private equity firms are heavily investing in data center operations, resulting in a surge of electricians and builders moving to areas where these massive facilities are constructed. Some local residents express concerns about potential adverse effects on their communities.
Tech giants are now demanding more computing power and electricity than ever, leading to ambitious plans. For instance, OpenAI aims to establish chip manufacturing plants in the Middle East to meet growing demand. Similarly, Google and Amazon have begun initiatives to develop advanced nuclear energy reactors to support their operations.
The Quest for More Power
At the core of AI’s rapid expansion is the increasing necessity for powerful computer chips. The specialized graphics processing units (GPUs) have become a cornerstone in this evolution. Originally designed for gaming graphics, GPUs excel at performing the complex calculations needed to operate neural networks, which support various AI applications, including chatbots.
Traditional central processing units (CPUs) handled numerous tasks but could process a single calculation at a time. In contrast, GPUs can perform numerous calculations simultaneously—a capability known as parallel processing. This efficiency allows AI systems to analyze extensive data sets far more quickly.
Innovations in Chip Design
To maximize the effectiveness of AI, tech companies began to use GPUs in significantly larger numbers. Notably, companies like Nvidia have modified their GPU designs to enhance processing capabilities further. Google, for its part, has also developed its own AI-centric chips. These chips focus specifically on processing tasks related to AI rather than general computing functions, allowing for more rapid advancements in machine learning.
Expanding Power and Cooling Needs
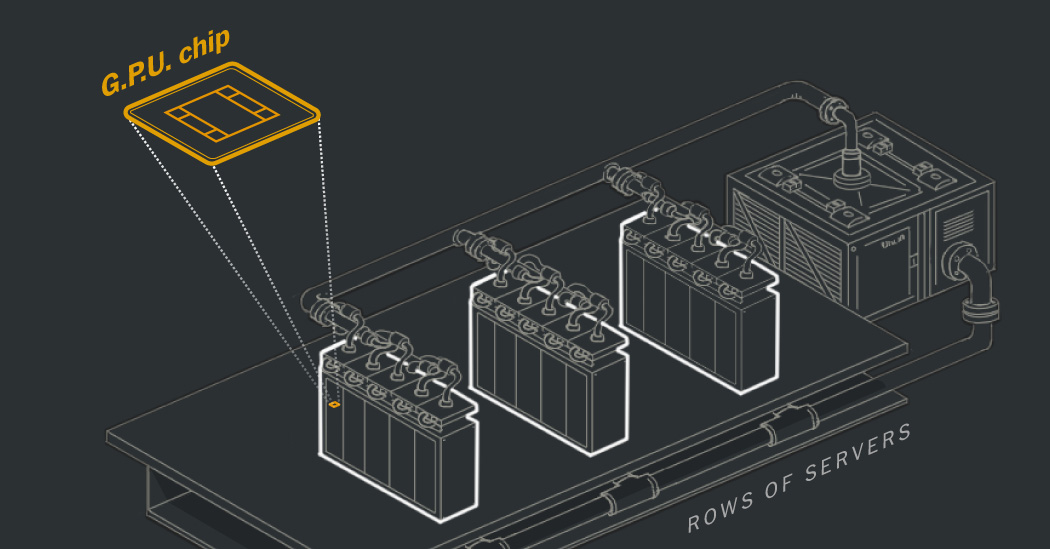
As data centers filled with GPUs are established, their demand for electricity is surging. For example, Cirrascale’s data center in Austin, Texas, previously required 5 megawatts to operate CPUs, which now only runs a fraction of the facility’s capacity packed with GPUs. Simultaneously, the energy consumption in data centers rose, accounting for over 4.4% of electricity use in the United States in 2023.
Moreover, cooling these advanced models poses another challenge. High-performance AI systems generate significant heat, leading to a need for innovative cooling methods. Companies now employ massive water-cooling systems as traditional air cooling is inadequate for the heat produced by densely packed chips.
Managing Water Resources
With the burgeoning heat generation, tech companies have adapted their cooling strategies. Google, for instance, runs cold water pipes adjacent to its chips to absorb heat effectively. However, relying on continuous water supply strains local resources, particularly in regions prone to drought. For example, Google data centers consumed over 6 billion gallons of water in 2023 alone.
Some companies have turned to advanced chillers to minimize water usage while still maintaining cooling efficiency. This approach can further increase energy demands but helps alleviate pressures on local water supplies.
Ongoing Developments
The momentum behind AI continues to grow; 2023 witnessed Google announcing plans to construct 11 new data centers across various states, while Meta is developing an expansive facility in Louisiana, remarking on the rapidly evolving landscape of AI technology.
The rapid pace of these changes reflects a paradigm shift in both computing and its surrounding infrastructure. The upcoming years will likely solidify the central role AI will play in shaping the future of technology, society, and the environment.